8.4. Analyzing Sustainability#
The earth is a complex non-linear system.
Linear system with independent variables

Non-linear system with interdependent variables
Scientific Concepts#
First law of Thermodynamics – conservation of energy - energy can neither be created nor destroyed it can only change form.
Matter and energy cannot disappear
Second law of Thermodynamics – entropy of a closed system cannot decrease
Matter and energy tend to disperse
All real systems have losses – thermal or mechanical
Additional Scientific Concepts#
With regard to many processes, Earth is a closed system
Value of matter is in its concentration and structure – energy density varies
All species of plants and animals are adapted to their environment – adaptation to change takes time
Limited resources/ non-renewable resources
Time scale matters
Assessment Methodologies#
Economic#
Cost / Benefit analysis
Modeling / regressions
Probability scenarios
Environmental#
Life-cycle analysis
Material flows
Resource accounting
Ecological foot print
NAMEA (National Accounting Matrix with Environmental Accounts) - a tool developed by EUROSTAT (the European Commission’s statistics service) to analyze relationships between the economy and the environment.
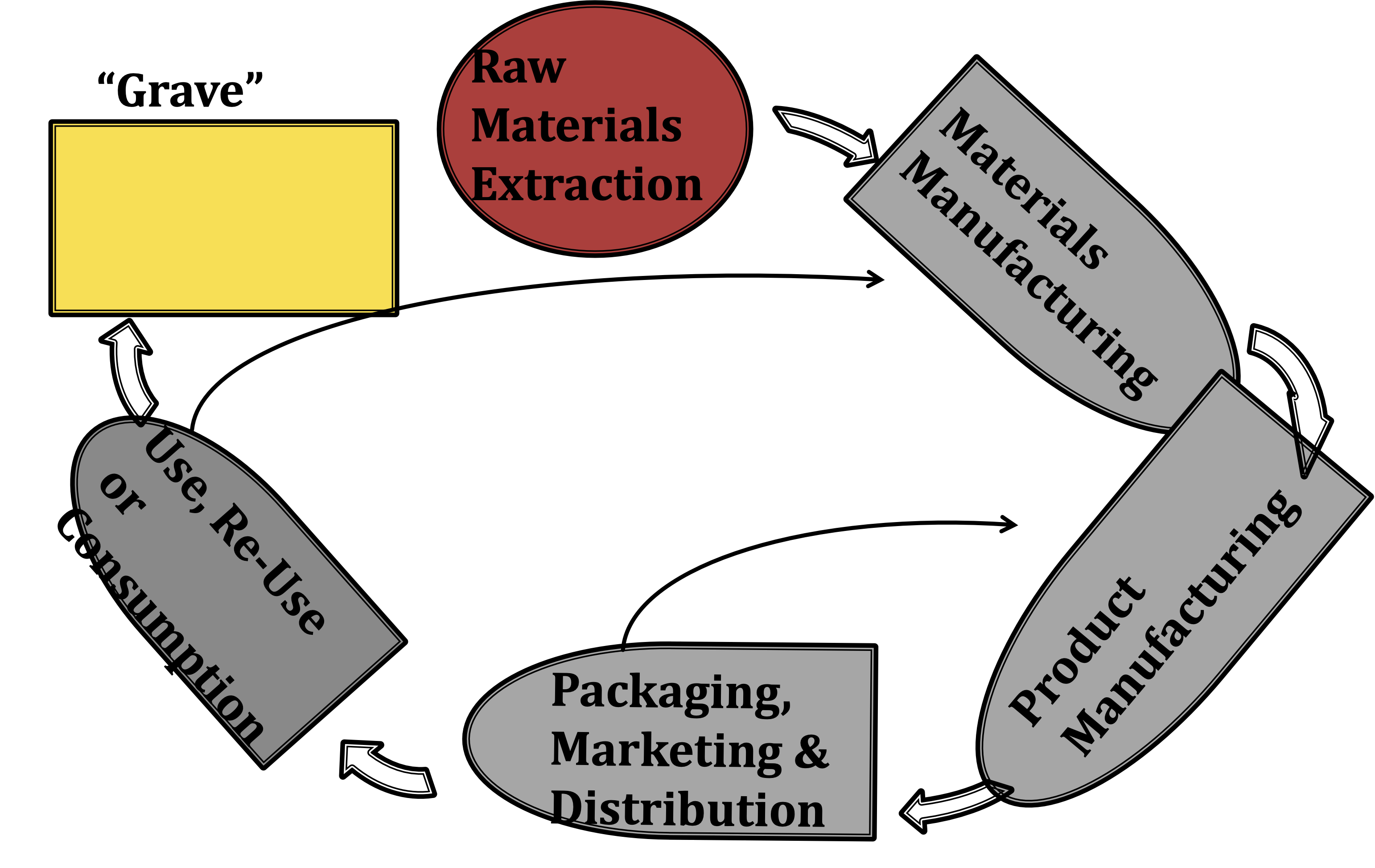
Life Cycle Analysis#
Design Life
Where did it come from?
How is it used?
Where will it go?
10 different ISO standards for Life-cycle assessment
“Zero Waste” and Cradle to Cradle Design#
Cradle to cradle design
A strategy for sustainability that aims to use all of the resources involved in production process and use them completely.
Works by taking what could be considered waste from one process and using it as inputs to other process.
Requires that all products be reusable or biologically de-gradable in a finite time frame
Carbon and Water Accounting#
The concept of a carbon footprint is to obtain a quantifiable impact of a business or persons activities on the environment by converting activities to an equivalent amount of carbon dioxide used. The units of measurement are tonnes or kilograms.
The total amount of water a person or business uses is defined as their water footprint.
A surprisingly large amount of water is need to produce the energy, food and products that we all use.
Carbon and Water Footprint Calculators#
US Government, Environmental Protection Agency Personal Emissions Calculator
EPA Carbon Footprint Calculator
Household Water Calculator

Social#
Sustainable livelihoods
Human and social capital evaluation
Participatory processes