4.2. Electricity Basics#
Learning Objectives#
By the end of this section you will be able to:
Describe the concept of electric charge
Describe electrical potential or voltage
Describe the flow of electric change that produces electric current
Electric Charge#
The smallest amount of electric charge that can exist is that of a single electron which has a charge of \(1.602 \times 10^{-19}\) C
A constant charge is usually denoted by Q, while a charge that changes with time is written as q or q(t).
Charge can be either positive or negative.
Dissimilar charges attract
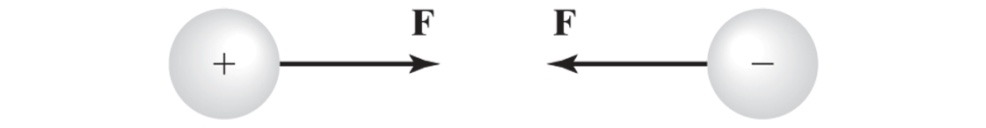
Similar charges repel

By the Electrostatic Force
When a particle has equal parts positive and negative charge it is electrically neutral.
When there is an imbalance, the particle is electrically charged.
In conductors, a significant number of charged particles are free to move.
When charge moves through a material, an electric current exists in the material.
However, unless an external force is applied, the electric charges in a conductor move about at random in an electric field.
Voltage#
Once an electromotive force is applied, charges move in a unified manner.
The electric potential difference, or voltage V, between two points is work done in moving a charge from one point to the other.
The instantaneous voltage \(v\) is described as a derivative
In SI the unit for electric potential is the volt, \(V\)
Current#
Electric current, \(I\), is the rate at which charge flows through an area.
The instantaneous current is written as a derivative
The SI unit for electric current is the ampere (A) and it is defined as
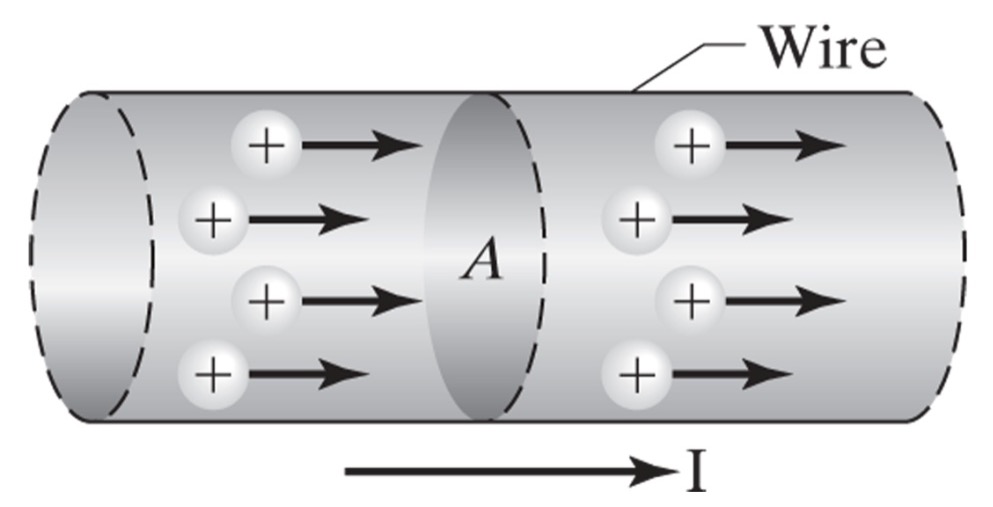
Convensional Current#
Conventional Current – based on the flow of positive charges, flows from positive to negative.
Conventional current is generally used in circuit analysis.
Electron Current#
Electron Current – the movement of free electrons from negative to positive.
Direct Current#
Direct Current (DC) - direction of charge flow is always the same
Alternating Current#
Alternating Current (AC) - direction of charge flow alternates in direction, often sinusoidal.
