Install Nginx
Now that the domain name is set up, and we have our SSL keys, the next step is to install and configure Nginx.
Nginx is an open-source web server that can handle many concurrent web connections at the same time. For the Nginx installation, I followed this tutorial from Digital Ocean.
Use PuTTY to connect to the server with the non-root sudo user peter we set up before. Once logged in, we can update the system and install Nginx.
$ sudo apt-get update
$ sudo apt-get upgrade
$ sudo apt-get install nginx
Digital Ocean installs a firewall application called ufw. Check out which apps the ufw firewall can work with:
$ sudo ufw app list
We see a list of available ufw configurations to work with Nginx:
Available applications:
Nginx Full
Nginx HTTP
Nginx HTTPS
OpenSSH
We want to allow in both http and https requests. Once a http request comes in, we'll use Nginx to convert the http connection to a https connection.
Select nginx full. Note the Capitalization in the command:
$ sudo ufw allow 'Nginx Full'
We can check out which ports ufw is allowing through with:
$ sudo ufw status
Note the output shows ufw allows Nginx Full and requests over port 8000. We opened port 8000 earlier, so we could see how JupyterHub works without a domain name or SSL. Once we get Nginx running and hooked up to JupyterHub, we need to remember to close off port 8000 in ufw.
Status: active
To Action From
-- ------ ----
22 LIMIT Anywhere
2375/tcp ALLOW Anywhere
2376/tcp ALLOW Anywhere
8000 ALLOW Anywhere
Nginx Full ALLOW Anywhere
22 (v6) LIMIT Anywhere (v6)
2375/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
2376/tcp (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
8000 (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Nginx Full (v6) ALLOW Anywhere (v6)
Nginx will start running as soon at it is installed. We can see the status with:
$ sudo systemctl status nginx
In the output, we should see something like below. This mean Nginx is running. Key in [ctrl-c] to exit the status dashboard.
Active: active (running) since Thu 2018-05-17 04:51:16 UTC; 15min ago
Main PID: 17126 (nginx)
CGroup: /system.slice/nginx.service
├── 17126 nginx: master process /usr/sbin/nginx -g daemon on; master_pr
└── 17127 nginx: worker process
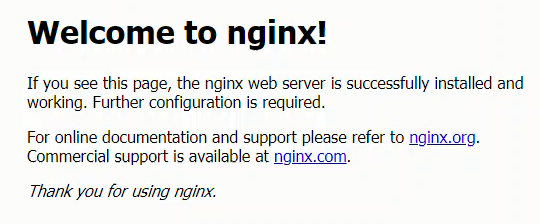
Now we can browse over to the domain (the domain we set up with Digital Ocean DNS and Doogle Domains) and see the Nginx start page.
Next Steps
Now that Nginx is installed, the next step is to configure Nginx to use our SSL certificate and run as a reverse proxy for our JupyterHub server.